Showing posts with label KDU. Show all posts
Showing posts with label KDU. Show all posts
C++ Classes.
Helllooo.... Readers... Welcome to inspire++. How are you my technical nerdy followers. The week before Last week was awesome. Thanks to the seniors from mechatronics.. We had a awesome workshop on robotics.. All the circuits, cool robots, drones you presented, the actual circuits we created using arduino boards most importantly the programming challenges you gave us !!! Truly seniors!! You did great. That was a day to remember.. :)
That been said.. Owkayy!! Lets Jump in to the lesson today!!
Classes.
The main purpose of C++ programming is to add object orientation to the C programming language and classes are the central feature of C++ that supports object-oriented programming and are often called user-defined types.
Last week we talked what are objects. An object is an entity (Real world thing). In programming , an object is a thing either from the perspective of the user of the software or the programmer.
* Object has two components, Properties and Behaviors.
Classes on the other hand known as blueprints (Plans) of objects. It's just like house planing. You build a house according to the plan. You can build as many houses as you want using the same plan, if you want to. For each house, you don't want to make a new plan.
In a program when you want to create an object, first what you have to do is create a class of that object. Then use the name of that class to create objects.
For example , think you have to make a software to a company to record the details about their customers. So a customer has a name , company gives him a customer ID, From when this person is a customer of the company..etc, And the customer buy things , customer may be given a discount by company.
Ok.. When you look at this scene what you have to keep in mind is that there are more than one customer in a company (more than 1000 maybe). So you have to see that there is a pattern. The best thing to do is take all the common factors of each customer and make it an object. Means, Create a object to the customer.
Right! , to create an object what we have to do is, as I mentioned earlier , create a class. Ok.. Now what I'm going to do is , create a class called customer. Let's see how to do that.
First Create the class.
Then type the keyword public inside the class.
Look!! There is a Colon : after public!! (Not a semi Colon!! ; )
Under public , define all the variables you want.
Ok! We have finished creating the class. Now it's time to create an object using that class (plan). Here's how you do it.
In main function, type the class name and leave a space ,and give a new name to your object (C1).
In main function, type the class name and leave a space ,and give a new name to your object (C1).
Then here's how you use the properties of that object.
Did you got the idea. Ok! Just like that we can create any amount of objects we want.
See how simple the idea is. OK.. Now I want you to practice this concept. So here are some examples. I will give you the answers in the next post.
Practice:
Create a Class named Box. Add variables Height , width , breadth. Create three Box objects in main function using that class. Give different values to the each object. Write a program to print the volumes of each box.
See you guys soon. Bye bye..!! :)
Answers for the First Semester Exam
Hey there.. Folks.. I'm Back after 1st sem exams.. Back in Action... ;) But, Still I can't take my mind out of the exams.. So I decided to do a post about the exam paper.. Hope this will important to my blog readers.. :)
a.)
This paper was included with 4 questions, and had to answer all of them. Lets start from the first one.
Q1.
a.) This is a theoretical question about programming. I copied this answer-phrase from my previous post.
Types of Programming Errors.
- Syntax Error
- This happens when we type incorrect codes, (ex: Missing Semi Colon ; , misspell a variable name, forget to close a Bracket } , )These programs can not compile, it shows an error message.
- Logical Error.
- This error occur due to our misunderstanding of the programming logic,These programs compile without producing any error messages, but does something totally different other than what we expected from the program.(To get a total, instead of addition + we type multiplication * , this doesn't give any error message, but give an unwanted result.)
- Runtime Error.
- Programs with this error also compile without any error message until some error occur in runtime.
- Ex :- Devide by zero in runtime.
(i) Syntax Error
(ii) Logical Error
(iii) Runtime Error
c.)
(i) This statement is 'True' because in any program language the codes are executed line by line, so
without the declaration-part reads first, the program
doesn't know what is the variable is.
(ii) This is 'False' because, c++ is case sensitive. The variable name value with lower case letters and
the variable name VALUE with upper case letters
are not identical in c++, means both variables can be exist at the same time.
(iii) This is also 'True' because when 2 integers are divided there might be a remainder for that division. If any two of decimal numbers are divided
(Floats) the answer is also a decimal point number,
there won't be any remainder for that division.
d.)
In this program there are 3 inputs, and we want to find the largest one only. so what we do is, we compare two numbers first and get the largest from those two and compare that with the other remaining number.(we need not to find the order of numbers , just the largest one only) To do that we need three selection conditions, one input and three output diagrams.
Q2.
a.)
In this question what you have to do is create some names for some variables they have given, using the rules and etiquette we have taught.
(i) float speed , float Speed , float spd ,.. etc.
(ii) char Grade , char grade , char grades , char Grades , char Grad...etc
(iii) float selPrice , float sel_price ,...etc
b.)
(i) int sum ;
(ii) count = 0 ;
(iii) cout<<" The average is: "<<avg ;
or
cout<<"\" The average is: \" "<<avg ;
c.)
(i) False- Even without the default case the switch works without producing any error, but in most cases default is
very essential part of the switch.
(ii) False - Precedence of arithmetic operators are higher.
Here's the order of precedence of operators.
(iii) True- because || operator is the Logical OR operator.
d.)
Q3.
a.)
(i) while loop
do while loop
for loop
(ii) The while loop and the for loop are both entry-condition loops. The test condition is checked before each iteration of the loop, so it is possible for the statements in the loop to never execute.
Exit-condition loop, in which the condition is checked after each iteration of the loop, guaranteeing that statements are executed at least once. This variety is called a do while loop
(b)
(i) 2 1.5 1 0.5
(ii) 10
7
4
1
(iii) 10
(c)
Q4.
a.)
(i) score
(ii) double
(iii) 10
b.)
A function has 2 main parts, Function Header and Function Body. As the features of a function we can consider few parts in detail,
- return type ex:- int , static , void , float, double
- function name ex:- int main () , double func1 ()
- parameter list ex:- int func1 (int num1, int num2)
- function body : rest of the function in curly braces
c.)
(i) int smallest (int x,int y,int z)
(ii) void instructions ()
(iii) double intToDouble (int number)
d.)
In above function the parameters(arguments) in function header x and y are declared with ampersands. int &x , int &y.This is because we want to pass the value to the function by reference.
That means when the values of the arguments are changed in the function, actual values of the reference variables are also changed.
Here I attached the complete program for you to try.
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
void zeroSmaller(int &x, int &y);
int main ()
{
int a;
int b;
cout<<"Enter a value for a"<<endl;
cin>>a;
cout<<"Enter a value for b"<<endl;
cin>>b;
zeroSmaller(a, b);
cout << "After value of a :" << a << endl;
cout << "After value of b :" << b << endl;
return 0;
}
void zeroSmaller(int &x, int &y)
{
if(x>y)
{
y=0;
}
else{x=0;}
return;
}
Here in function zeroSmaller, if x is lower then x will be set to zero by the function , but at the same time the actual value of a is also set to zero, because the value was passed by reference. And the value of b will be set to zero if the y is the lowest.
So that's all for the first semester exam. Hang around with my c++ programming posts series to learn this completely from the beginning.
If you have anything to be more explained please mention in comments section below or any good or bad thoughts about this blog please comment.
See you in my next post.. Happy vacation.. :)
Quick Post For 1st Semester Exam
Hey Guys.. This is a Quick Post to Discuss About the Model Paper of my Uni.. hope others will get something from this too..
Here I pasted the paper... And Down there I Discussed it...
That's all guys... Hope this will help you.. C..U after the exams.. Good luck.. :)
Here I pasted the paper... And Down there I Discussed it...
Question
01 (25
Marks)
(a) Differentiate
the machine language and the high level language. (5 Marks)
(b) Define the terms compiler and interpreter. (5 Marks)
(c) Describe
the different ways to include comments in a C++ source code. State whether the
comments are nested. (5 Marks)
(d) List
the three main kinds of program errors.
i.
Identify the error discovered, if you “misspell a variable or a function name”.
ii.
Identify the error discovered, if you “use
a single equal sign to check equality”.
(5
Marks)
(e) Write
a C++ program to display the following output. (5 Marks)
(Hint: Use escape sequences.)
Question 02 (25 Marks)
(a) The
following identifiers are written in C++ and some of them are syntactically
incorrect. Identify the syntactically incorrect identifier(s) and state the
reason. (5 * 1 = 5 Marks)
i.
CASE4
ii.
2010IncomeTax
iii.
sales$
iv.
exchange Rate
v.
cout
(b) Write
C++ expressions for the following mathematical formula. (5 Marks)
(c) Determine
the value of each of the following expressions, if x = 5, y = 10 and z = -6.
Write your steps clearly. (5
Marks)
i.
y > 15 && z < x + y
ii.
! ( y <= 12 ) || x % 2 == 0
(d) Illustrate
the outputs of the following program segments. (5
* 2 = 10 Marks)
i.
|
int num1,
num2, sum;
num1 = 5;
num2 = 4;
sum =
num1 + num2;
cout
<< "The sum of ";
cout.width(2);
cout
<< num1 << " and " << num2;
cout
<< "is" << sum << "\n";
|
|
float
value1, value2, product;
value1 =
5.31;
value2 =
7.8;
product =
value1 * value2;
cout.setf(ios::fixed);
cout.setf(ios::showpoint);
cout.precision(2);
cout
<< "The Product of\n" << value1 <<
"and";
cout
<< value2 << "is\n" << setw(14) <<
product;
|
ii.
Question 03 (25
Marks)
You are required to implement a program to handle customer
sales of a fruits stall at Katubedda Super Market. Write a program in C++ to
calculate the amount of price and print a bill for the customer. Your program
should allow:
(a) To
input a number of items bought (quantity) and the price per item (unit price). (5 Marks)
(b) Calculate
the total cost; give discount to the customer according to the following
conditions.
(5 Marks)
If the customer bill amount is greater than Rs.500/=,
will be having a 2.5% discount.
If the customer bill amount is greater than Rs.750/=,
will be having a 3% discount.
If the customer bill amount is greater than Rs.1000/=,
will be having a 5% discount.
(c) Your
program should ask for the amount of money tendered and print the correct amount of money change. (5 Marks)
(d) Print
an appropriate bill. The output should correct to two decimal places. (5 Marks)
(e) Your
program should allow doing the calculation as many times as the user wishes.
(Hint:
Use suitable C++ loop structure to implement this task.) (5 Marks)
Question 04 (25
Marks)
A competition is being
organized by StarCricket Club to select the most popular player for year 2015.
Nalaka, Amila, Saman, Ruwan and Chathura are five players who are contesting
for popularity. The players are numbered from 1 to 5 and voting is done by
entering the player number as an input.
Write a C++ program to
read the vote and to count the votes cast for each player using an array. In
case, a number read is outside the range (1..5), the vote should be considered
as a ‘spoilt vote’.
Your program
should include the following tasks.
(a)
Define an array called “vote” to store votes
of players. Initialized each array element into zero.
(5 Marks)
(b)
Read data into an array called “vote”.
(Nalaka’s votes are in the first element of the array, Amila’s votes are in the
second element of the array etc..) (5 Marks)
(Hint: Use switch statement to handle
the user selection.)
(c)
Your program should allow 100 club
members to cast their votes. (5 Marks)
(Hint: Use a suitable C++ loop structure to implement this
task.)
(d)
Calculate the
number of votes cast for each player, number of spoilt votes and total number
of votes. (5 Marks)
(e)
Print the number
of votes cast for each player, number of spoilt votes and total number of votes. (5 Marks)
END
OF PAPER
Q1.
a.) Difference between Machine Language and a high level language is ,
- A machine Language is a low level language which a computer can understand or computer's use machine language to work. ex:- Assembly
- On the Other hand a high Level Language is a programming language closer to human language or as humans high level languages are easy to understand and to work-with for us. ex:- java , c++
- compiler and interpreter both work as translators of a source code to a machine language.
- it means it translate the code we type using codeblocks into machine language.(like binary )
- Some Programming languages use compiler only i.e C, C++, some use interpreter i.e Python, Ruby, some use both.
- Compilers Translate the entire source code at once into machine code file, and then we can run our program any time we want. Compilers are Faster. Consume more memory. If there is any error in the code compilers are less accurate in finding them.
- Interpreters on the other hand translate the code line by line , consume more time, memory efficient, and accurate in finding errors in the code.
- Comments are lines of text we put in a code which does not effect to the code any how. We use comments to mention important things in a code. We can write anything as comments there are no limits.
- There are two types of comments in C++, Single line comments and Multi line comments.
- For Single line comments we put // , two backward slashes and we type the comment text in a single line.
- For multi line comments we put /* at the begining of the comment and we end the comment with */
- Nesting comments means put multi line comment in side another multi line comment. C++ does not support Nested comments.
- we can check that by
- int nest = /*/*/0*/**/1;
- cout<<nest;
- if the output is 1 , it supports nested comments and if output is 0 then it doesn't support.
- Compile Error (Syntax Error)
- This happens when we type incorrect codes, (ex: Missing Semi Colon ; , misspell a variable name, forget to close a Bracket } , )These programs can not compile, it shows an error message.
- Logical Error.
- This error occur due to our misunderstanding of the programming logic,These programs compile without producing any error messages, but does something totally different other than what we expected from the program.(To get a total, instead of addition + we type multiplication * , this doesn't give any error message, but give an unwanted result.)
- Runtime Error.
- Programs with this error also compile without any error message until some error occur in runtime.
- Ex :- Devide by zero in runtime.
- Syntax Error (Compile Error)
- Logical Error.
a.) Identifiers are the names we use when programming , (Names we use to name Variables , function , class etc..) An identifier starts with a letter A to Z or a to z or an underscore (_) followed by
zero or more letters, underscores, and digits (0 to 9).
Identifiers can't have !@#$%^&*()+=.. Only Underscore.
CASE4
2010IncomeTax
sales$ // $ Dollar Sign
exchange Rate // Space between two words
cout // cout is a function name, cant use as an identifier
b.)
c.)
&& - Logic AND % - Modulas (Remainder of a devision)
|| - Logic OR == - is equal to ??
! - Logic NOT
i)
= 10>15 && -6<15
= false && true
= false
ii)
= !(10 <= 12) || 5%2 == 0
= !true || false
= NOT (true) OR false
= false
d.)
i)
Q3.
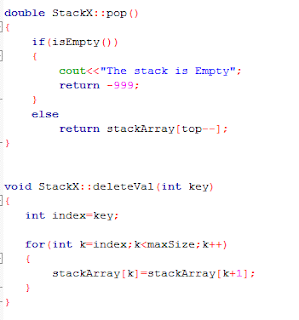
a.) Here I posted some Screen Shots from My Code. Some code parts have described with in comments.
 |
| (1) |
 |
| (2) |
 |
| (3) |
 |
| (4) |
Q4.
a.)
Here also I explained every part of codes in comments, in this example I have used an if else if statement to find the winner, which has not asked to do in question paper.
 |
| (1) |
 |
| (2) |
 |
| (3) |
 |
| (4) |
That's all guys... Hope this will help you.. C..U after the exams.. Good luck.. :)
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)
Life of a Systems Engineer
Hello, my dear readers. ✌😀✋ I'm talking to you after a very long time. And I am thrilled to talk-to and hear-from you after all thi...

-
Hello… People with Happy Faces.. Just right after finishing the Exams and having a Leisure time.. :) How you doing...
-
Let’s Start Coding. Hello Guys..!! Welcome to engineers favorite programming blog.. ;) Last week we started our little chat abou...